Chapter 2: Earth's Lithosphere
The goals and objectives of this chapter are to:
- Describe the basic structure of the earth and the role of the theory of plate tectonics plays in understanding movements of the crust.
- Explain the process of crustal development and the associated geologic hazards associated it.
- Identify the process of crustal erosion and degradation and the associated geologic hazards associated with it.
Theory of Plate Tectonics
|
STRUCTURE OF EARTH
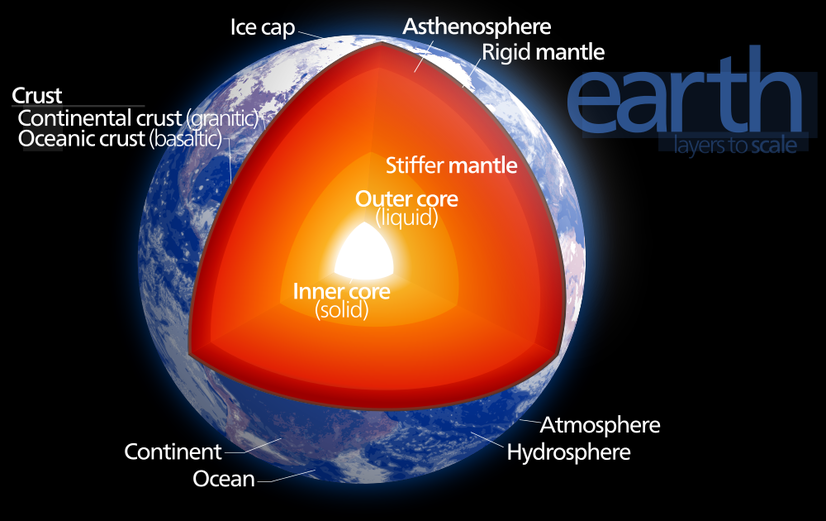
The earth consists of three layers: an inner and outer core, the mantle, and two types of crust. The earth's core consists of two parts: a liquid outer core and a solid inner core, both made of iron and nickel from the early make-up of the planet, and where the temperatures can range from 8,600 degrees to 9,600 degrees Fahrenheit. The next and largest layer is called the mantle, which makes up two-thirds of Earth's mass. The mantle is actually called a plastic solid, which means it has the ability to flow very slowly. Heat from the earth's core causes the mantle to convect, like water over a stove but much slower, and it is the mantle's convection that is the driving force of plate tectonics. |
The surface layer of the earth is called the crust and it makes up only 1 percent of Earth's mass. The crust is subdivided into two components: oceanic and continental crust. Again referring back to the image on the right, note that the oceanic crust is only about 3 miles thick, but is slightly more dense than continental crust. Most of this oceanic rock is called basalt and is a dark, dense rock. Continental crust is much thicker than oceanic crust (averages between 20 to 25 miles thick), but is actually slightly less dense than oceanic crust. The main type of rock on continents is called granite. So if these two types of crust were to collide into each other, what do you think would happen to the oceanic crust? As a whole, notice that the crust is lighter than the mantle. It is sometimes said that the crust "floats" on the mantle like an iceberg in water and that is not too far from the truth and is called isostacy. Finally, the crust is the coldest, most rigid, and brittle layer with lots of folds and fractures.
THEORY OF PLATE TECTONICS
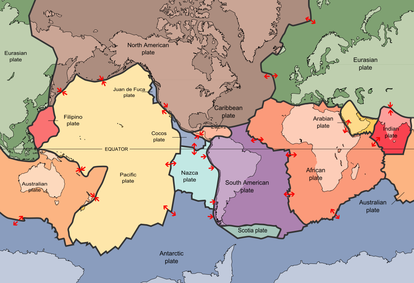
The driving force of earthquakes and volcanoes is described in the theory of plate tectonics. The theory states that the earth is made of several tectonic plates along with several smaller plates. Each tectonic plate consists of oceanic and continental crust that move around the earth's surface like bumper cars because of convection within the mantle.
The theory also explains that the majority of earth's earthquakes and volcanoes occur along the boundaries of these tectonic plates as they either grind past or underneath each other.
The driving force of earthquakes and volcanoes is described in the theory of plate tectonics. The theory states that the earth is made of several tectonic plates along with several smaller plates. Each tectonic plate consists of oceanic and continental crust that move around the earth's surface like bumper cars because of convection within the mantle.
The theory also explains that the majority of earth's earthquakes and volcanoes occur along the boundaries of these tectonic plates as they either grind past or underneath each other.
|
|
|
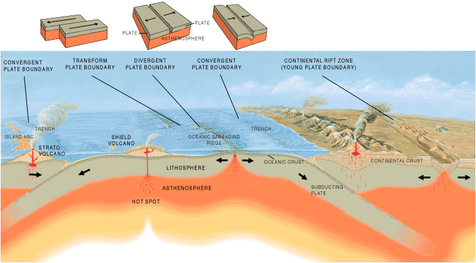
There are three major types of tectonic plate boundaries: convergent, divergent, and transform. Let's first look at convergent plate boundaries, which can be broken down into three subcategories.
Recall that oceanic crust is denser than continental rock like granite. Thus when two tectonic plates collide, the denser oceanic crust will subduct underneath the lighter continental crust. If the subducting rock becomes stuck, vast amounts of energy builds up. But once the pressure and energy is too great, the rock will rupture creating powerful earthquakes. As the subducted material sinks further, it will begin to melt under great heat and pressure, becoming less dense as it melts, and rise up as magma to form dangerous composite volcanoes. Mountain ranges created by oceanic-to-continental convergence are the Andes mountains in South America, the Cascades in the western United States, and the Ring of Fire in the Pacific Ocean.
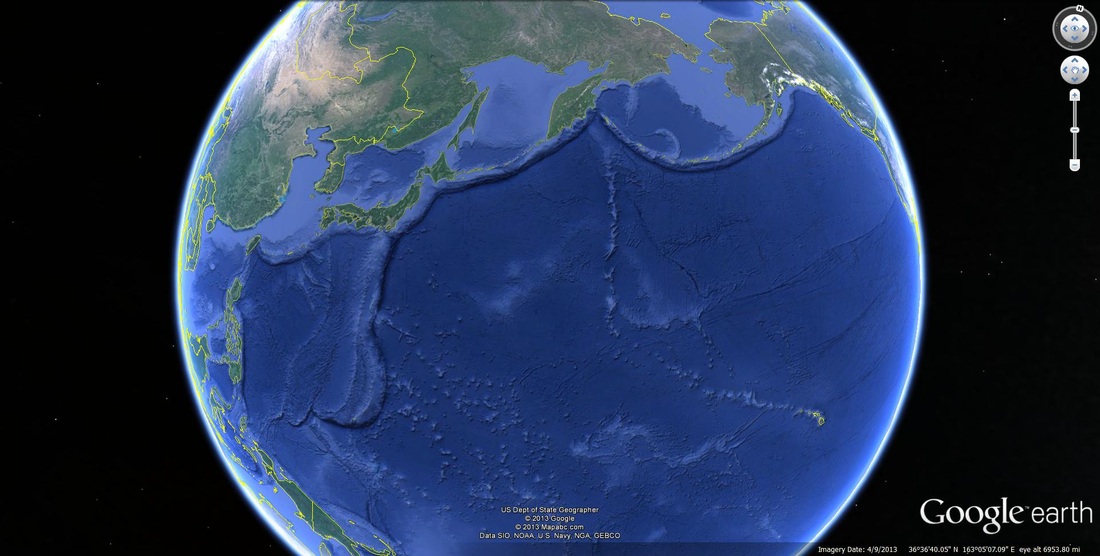
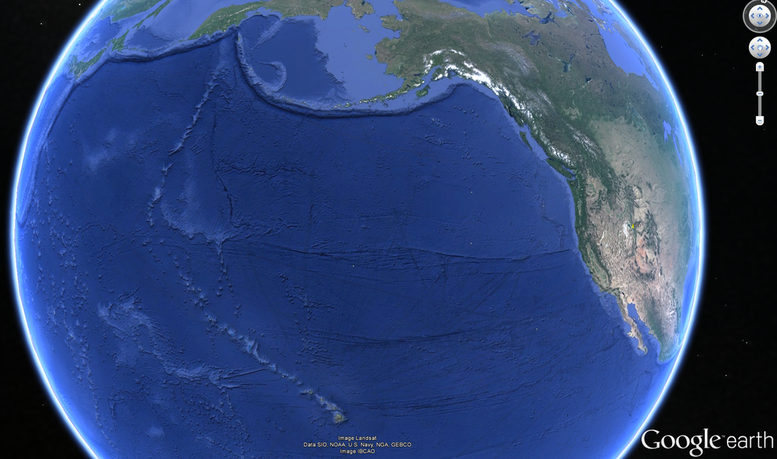
Below is a Google Earth image showing a series of oceanic-to-oceanic subduction zones within the Pacific Ring of Fire. You can visibly see the subduciton zones that create the volcanic and powerful Aleutian Islands and the converging subduction plates that make of volcanic islands of Japan.
With oceanic-to-oceanic convergence, the heavier of the two will subduct down beneath the other. Just like continental-to-oceanic convergence, this plate boundary can generate powerful earthquakes and volcanoes; but instead of volcanoes on land, volcanic islands form such as Japan, the Aleutian Islands of Alaska, and Indonesia. The great earthquake in Indonesia in 2004, which produced the devastating tsunami, was created by this process along with the 2011 earthquake and tsunami in Japan.
Recall that oceanic crust is denser than continental rock like granite. Thus when two tectonic plates collide, the denser oceanic crust will subduct underneath the lighter continental crust. If the subducting rock becomes stuck, vast amounts of energy builds up. But once the pressure and energy is too great, the rock will rupture creating powerful earthquakes. As the subducted material sinks further, it will begin to melt under great heat and pressure, becoming less dense as it melts, and rise up as magma to form dangerous composite volcanoes. Mountain ranges created by oceanic-to-continental convergence are the Andes mountains in South America, the Cascades in the western United States, and the Ring of Fire in the Pacific Ocean.
Below is a Google Earth image showing a series of oceanic-to-oceanic subduction zones within the Pacific Ring of Fire. You can visibly see the subduciton zones that create the volcanic and powerful Aleutian Islands and the converging subduction plates that make of volcanic islands of Japan.
With oceanic-to-oceanic convergence, the heavier of the two will subduct down beneath the other. Just like continental-to-oceanic convergence, this plate boundary can generate powerful earthquakes and volcanoes; but instead of volcanoes on land, volcanic islands form such as Japan, the Aleutian Islands of Alaska, and Indonesia. The great earthquake in Indonesia in 2004, which produced the devastating tsunami, was created by this process along with the 2011 earthquake and tsunami in Japan.

When two continental plates converge, instead of subduction, the two similar tectonic plates will buckle up to create large mountain ranges like a massive car pile-up. This is called continental-to-continental convergence, and geologically creates intense folding and faulting rather than volcanic activity. Examples of mountain ranges created by this process are the Himalayan mountains (taken from the International Space Station) as India is colliding with Asia, the Alps in Europe, and the Appalacian mountains in the United States as the North American plate collided with the African plate when Pangea was forming. The Kashmir India earthquake of 2005 that killed over 80,000 people occurred because of this process. And most recently, the 2008 earthquake in China which killed nearly 85,000 people before the Summer Olympics was because of this tectonic force.
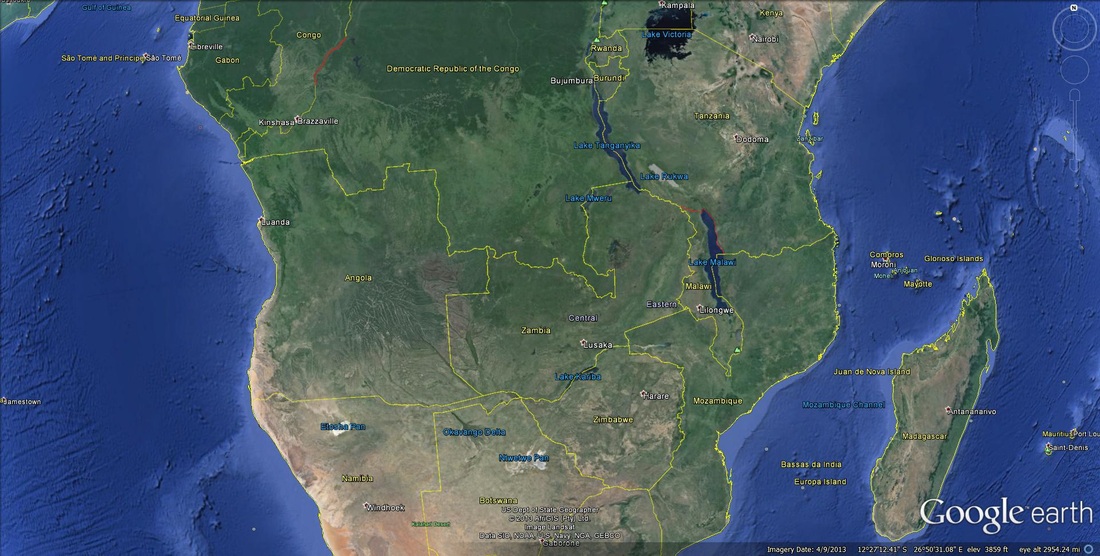
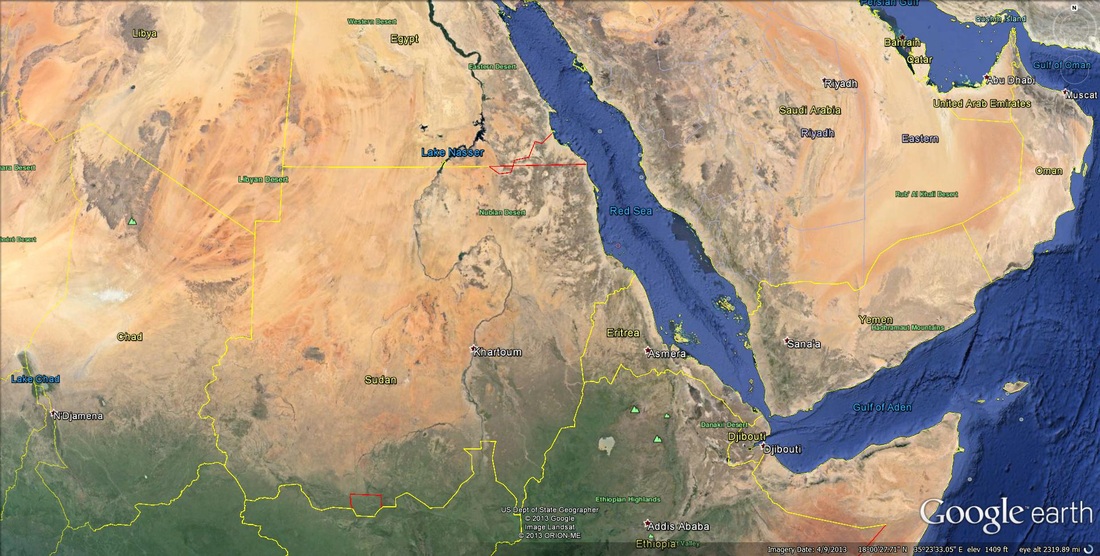
When two tectonic plates move away from each other, or when a tectonic plate tears itself apart, divergent boundaries can form. As divergence occurs, shallow earthquakes can occur along with volcanoes along the rift areas. When the process begins, a valley will develop such as the Great Rift Valley in Africa. Over time that valley can fill up with water creating linear lakes. If divergence continues, a sea can form like the Red Sea and finally an ocean like the Atlantic Ocean. Check out the eastern half of Africa and notice the lakes that look linear. Eastern Africa is tearing apart from these linear lakes, to the Great Rift Valley, and up to the Red Sea. Notice how the Red Sea looks like it could be put back together again. The ultimate divergent boundary is the Atlantic Ocean, which began when Pangaea broke apart.
Below are two satellite images using Google Earth, both focusing on parts of Africa. On the left yo can see rift valleys that have filled in with water to form linear lakes. On the right in northern Africa, you can see the Red Sea with a rift valley in the center, which use to be a linear lake that grew into a sea. If the Red Sea continues to grow, it could form an ocean similar to the Atlantic Ocean with the mid-Atlantic Ridge.
Below are two satellite images using Google Earth, both focusing on parts of Africa. On the left yo can see rift valleys that have filled in with water to form linear lakes. On the right in northern Africa, you can see the Red Sea with a rift valley in the center, which use to be a linear lake that grew into a sea. If the Red Sea continues to grow, it could form an ocean similar to the Atlantic Ocean with the mid-Atlantic Ridge.
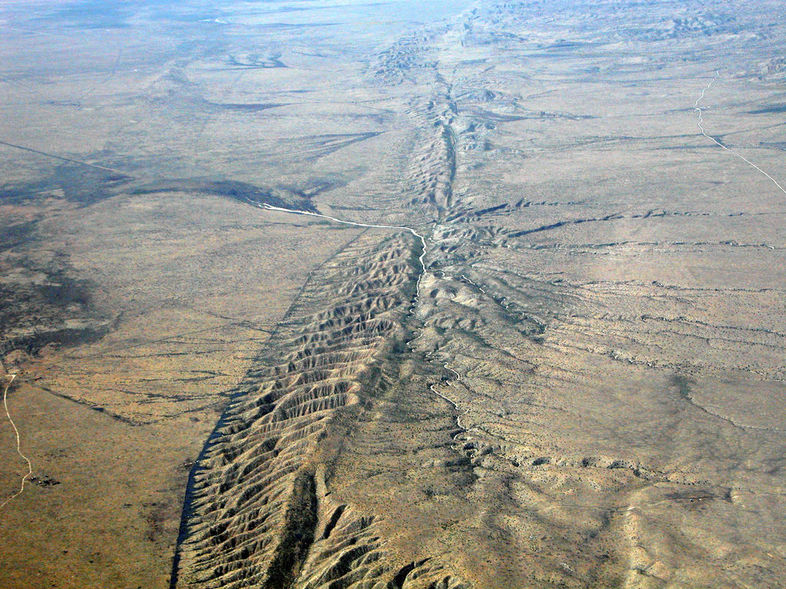
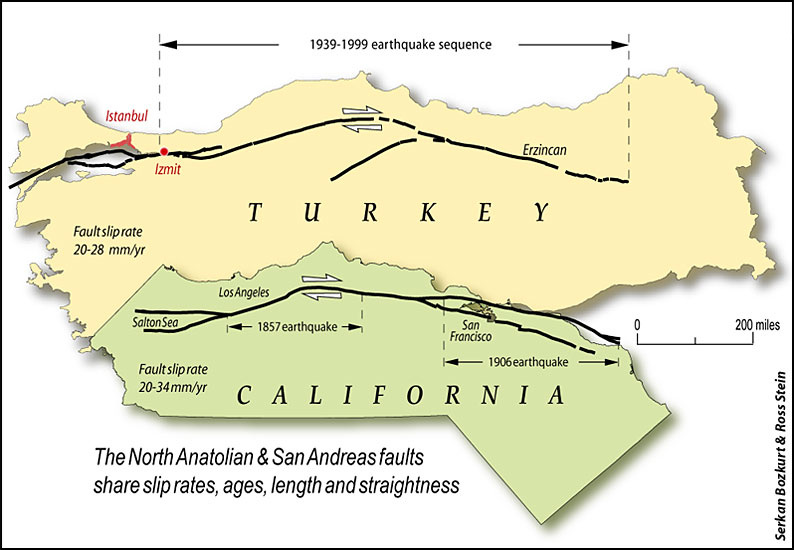
Transform boundaries occurs when two tectonic plates slide (or grind) past parallel to each other. The most famous transform boundary is the San Andreas Fault where the Pacific plate (that Los Angeles and Hawaii are on) is grinding past the North American plate (that San Francisco and the rest of the United States is on) at the rate of 3 inches a year. Recently, geologists have stated that San Francisco should expect another disastrous earthquake in the next 30 years. Another important transform boundary is the North Anatolian Fault in Turkey. This powerful fault last ruptured in 1999 in Izmit, Turkey which killed 17,000 people in 48 seconds.
Geologic Hazards

EARTHQUAKES
An earthquake is a sudden motion or trembling in the earth caused by the abrupt release of slowly accumulated energy. All earthquakes occur along a fault, which is a fracture in the earth's crust where tectonic movement occurs. Where the actual break occurred along the fault is called the focus (also called the hypocenter) and the epicenter is the point on the Earth's surface that lies directly above the focus and is where the strongest shockwave is normally felt. Click here to watch a brief video on earthquakes.
Recall that all around the planet, tectonic plates are moving because of convection in the mantle. Tectonic plates are also composed of two types of crust, oceanic and continental. The oceanic crust, which is made mostly of basalt is more dense than continental crust that is made of granite. When these tectonic plates come in contact, the denser oceanic crust subducts below the continental crust. Now sometimes when two tectonic plate come in contact they become stuck. As the rocks begin to bend or strain under tectonic forces, large amounts of energy, called strain, builds. When the stress becomes too great for the rocks to hold, segments may suddenly snap, releasing large amounts of energy, called the elastic rebound theory.
An earthquake is a sudden motion or trembling in the earth caused by the abrupt release of slowly accumulated energy. All earthquakes occur along a fault, which is a fracture in the earth's crust where tectonic movement occurs. Where the actual break occurred along the fault is called the focus (also called the hypocenter) and the epicenter is the point on the Earth's surface that lies directly above the focus and is where the strongest shockwave is normally felt. Click here to watch a brief video on earthquakes.
Recall that all around the planet, tectonic plates are moving because of convection in the mantle. Tectonic plates are also composed of two types of crust, oceanic and continental. The oceanic crust, which is made mostly of basalt is more dense than continental crust that is made of granite. When these tectonic plates come in contact, the denser oceanic crust subducts below the continental crust. Now sometimes when two tectonic plate come in contact they become stuck. As the rocks begin to bend or strain under tectonic forces, large amounts of energy, called strain, builds. When the stress becomes too great for the rocks to hold, segments may suddenly snap, releasing large amounts of energy, called the elastic rebound theory.
|
|
|
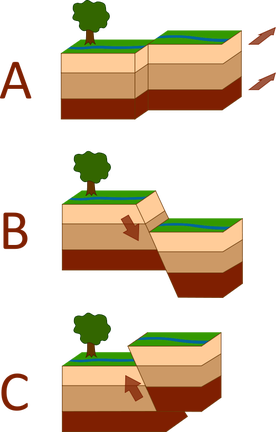
There are several types of faults that earthquakes occur on, which are dependent on whether the fault is occurring because of convergent, divergent, or transform tectonic plate forcing. Geologists use old mining terms to distinguish between different types of faults. Think of a minor walking down into the earth along a fault line. The ground the miner is walking on is called the foot-wall. If the minor needs to hand their lantern, the ceiling is called the hanging-wall.
Strike-slip faults (A) occur along transform boundaries where tectonic plates are moving horizontal or parallel to each other. Deformation of rivers, roads, fences, etc. can occur if they cross over these fault lines. Examples of strike-slip faults are the San Andreas Fault in the United States and the North Anatolian Fault in Turkey.
Normal faults (B) are common along divergent plate boundaries. As extensional forces occur, the foot-wall is forced upward, while the hanging wall slides downward. This can create a series of valleys (called a graben) and mountains (called a horst). Examples of mountain ranges and valleys created by normal faulting are theGrand Tetons, the Basin and Range in the western United States, and the Wasatch Front in Utah.
Reverse faults (C) are caused by compressional forces as tectonic plates collide together forcing one plate to rise above another. Using the mining terminology, movement along a reverse fault would cause the hanging-wall to rise up and the foot-wall to drop lower. The angle of a reverse fault is about 45 degrees, but if the angle of the fault is steeper than 45 degrees it is called a thrust fault. When two plates collide, intense folding and faulting can occur. Examples of where reverse and thrust faults occur are where convergent boundaries are common such as: the Northern Rocky Mountains, the Alps, Himalayas, and the Appalachian mountains.
Strike-slip faults (A) occur along transform boundaries where tectonic plates are moving horizontal or parallel to each other. Deformation of rivers, roads, fences, etc. can occur if they cross over these fault lines. Examples of strike-slip faults are the San Andreas Fault in the United States and the North Anatolian Fault in Turkey.
Normal faults (B) are common along divergent plate boundaries. As extensional forces occur, the foot-wall is forced upward, while the hanging wall slides downward. This can create a series of valleys (called a graben) and mountains (called a horst). Examples of mountain ranges and valleys created by normal faulting are theGrand Tetons, the Basin and Range in the western United States, and the Wasatch Front in Utah.
Reverse faults (C) are caused by compressional forces as tectonic plates collide together forcing one plate to rise above another. Using the mining terminology, movement along a reverse fault would cause the hanging-wall to rise up and the foot-wall to drop lower. The angle of a reverse fault is about 45 degrees, but if the angle of the fault is steeper than 45 degrees it is called a thrust fault. When two plates collide, intense folding and faulting can occur. Examples of where reverse and thrust faults occur are where convergent boundaries are common such as: the Northern Rocky Mountains, the Alps, Himalayas, and the Appalachian mountains.
VOLCANOES
Earth is made up of a series of tectonic plates, each consisting of oceanic basalt and continental granite. Now because of convection within the mantle, new oceanic crust is created at divergent boundaries creating oceanic ridges. Where tectonic plates converge, the denser oceanic basalt subducts below the lighter continental granite. As the oceanic crust subducts deep enough it begins to melt under great heat and pressure to form molten rock called magma. The molten rock is less dense than the surrounding rock and thus rises to the surface to create volcanoes. Magma cools into rock much slower than on the surface because the heat gets trapped. Because of this, when magma reaches the surface, geologists call it lava.
Earth is made up of a series of tectonic plates, each consisting of oceanic basalt and continental granite. Now because of convection within the mantle, new oceanic crust is created at divergent boundaries creating oceanic ridges. Where tectonic plates converge, the denser oceanic basalt subducts below the lighter continental granite. As the oceanic crust subducts deep enough it begins to melt under great heat and pressure to form molten rock called magma. The molten rock is less dense than the surrounding rock and thus rises to the surface to create volcanoes. Magma cools into rock much slower than on the surface because the heat gets trapped. Because of this, when magma reaches the surface, geologists call it lava.
|
|
|
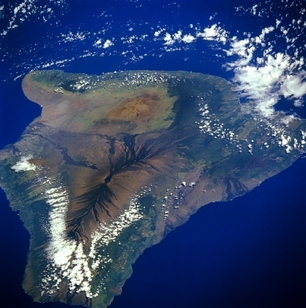
Shield volcanoes tend to be the tallest volcanoes - and even the tallest mountains - in the world. These volcanoes tend to have gentle slopes with an arc in the shape of a Roman shield. It is their low viscosity lava flows that produces the gentle slopes. Eruptions tend to be mild in comparison to other volcanoes, but lava flows can destroy property and vegetation. The low viscosity magma can flow not only on the surface as lava, but also underground in lava tubes. The most well known shield volcano is Hawaii. There are two types of lava flows, pahoehoe which is a ropy type of lava that flows easily (low viscosity). The other type is called aa and is a blocky type of lava and has a higher viscosity and does not like to flow well.

Cinder cone volcanoes are the smallest type of volcanoes ranging from 300 to 650 feet high. The volcano is built up by eruptions of solid pyroclastic material, specifically tephra, along the volcanic neck. Many people live near cinder volcanoes because the weathered pyroclastic material becomes fertile soil for agriculture. These volcanoes kill few people, but can destroy property.

Composite volcanoes are some of the most dangerous volcanoes on the planet. They tend to occur along oceanic-to-continental and oceanic-to-oceanic convergent boundaries which produces highly viscous pyroclastic material that erupts violently when it reaches the surface. They are also called stratovolcanoes or andesite volcanoes because they erupt volcanic rock - called andesite - which builds up the volcano followed by lava which holds the material in place. This creates stratified layers within the volcano. Examples of composite volcanoes include Mount St. Helens, Mount Rainer, and Mount Pinatubo. Here's a great time-lapse of Mount St. Helens from NASA's Earth Observatory from 1979 to 2013.
Composite volcanoes and other violent volcanos can erupt so violently that they sometimes collapse in on themselves or actually blow themselves up to produce calderas. One of the most powerful volcanoes in the world - Yellowstone - is a massive caldera that has collapsed several times. Sometimes these calderas can fill up with water to produce beautiful lakes such as Mount Mazama (Crater Lake), in Oregon.
Composite volcanoes and other violent volcanos can erupt so violently that they sometimes collapse in on themselves or actually blow themselves up to produce calderas. One of the most powerful volcanoes in the world - Yellowstone - is a massive caldera that has collapsed several times. Sometimes these calderas can fill up with water to produce beautiful lakes such as Mount Mazama (Crater Lake), in Oregon.

The theory of plate tectonics could never explain why some volcanoes form away from any tectonic plate boundaries. These anomaly volcanoes are called hot spots. Instead, they tend to form within tectonic plates in areas where the lithosphere is weak, which allows magma to rise up to the surface to create volcanoes. Though convection within the mantle causes tectonic plates to move, the hot spot does not. The hot spot stays stationary while the tectonic plate moves across it. Examples of hot spots include Hawaii and Yellowstone.
Hawaii is a shield volcano on top of a hot spot. It is a series of volcanic islands that have been created as the Pacific Plate has moved across the hot spot. Hawaii has gentle slopes and is the most active volcano in the world.
Hawaii is a shield volcano on top of a hot spot. It is a series of volcanic islands that have been created as the Pacific Plate has moved across the hot spot. Hawaii has gentle slopes and is the most active volcano in the world.
Weathering and Erosion
For much of this chapter, we've been looking at Earth's internal forces through the scientific theory of plate tectonics. Recall that the driving mechanism of these internal forces is convection within the mantle. We will now spend a little amount of time looking at external forces that specifically deal with weathering, erosion, and mass wasting. Let's first start with some definitions. Weathering is the physical breakdown and chemical alteration of rock at or near Earth's surface. Erosion occurs when the weathered material is physically removed by water, wind, or ice from it's weathered position. Mass wasting is similar to erosion, where the weathered material is transferred downslope under the influence of gravity and lack of friction. Let's now look at these in more detail.
MECHANICAL WEATHERING
Mechanical weathering (sometimes called physical weathering) occurs when physical forces break rocks down into smaller pieces. Within the overall process of mechanical weathering, there are five sub-categories: frost wedging, salt crystal growth, sheeting, thermal expansion and biological activity.
Frost wedging is a very common type of mechanical weathering in mountainous regions. During the fall and spring months, daytime temperatures can rise above freezing and at night dip below freezing. During the daytime, any moisture on a rock can slip into the cracks as liquid. At night, that liquid can freeze and expand breaking the rock like a small wedge. The following day, the ice melts deeper into the crack so that it can wedge again that night.
Mechanical weathering (sometimes called physical weathering) occurs when physical forces break rocks down into smaller pieces. Within the overall process of mechanical weathering, there are five sub-categories: frost wedging, salt crystal growth, sheeting, thermal expansion and biological activity.
Frost wedging is a very common type of mechanical weathering in mountainous regions. During the fall and spring months, daytime temperatures can rise above freezing and at night dip below freezing. During the daytime, any moisture on a rock can slip into the cracks as liquid. At night, that liquid can freeze and expand breaking the rock like a small wedge. The following day, the ice melts deeper into the crack so that it can wedge again that night.

Salt crystal growth is a common occurrence near large bodies of salt water like the ocean and some lakes like the Great Salt Lake or the Dead Sea. When sea spray breaks onto rocks, the dissolved salt can sink within the cracks. When the water evaporates, it leaves behind the crystalized salt. As more salt water comes, the crystals can grow and push on the rock cracks causing them to break more and possibly fracture.
Sheeting occurs when large igneous rock are exposed by erosion processes. As the overlying pressure is removed from the rock, it is allowed to expand and break off in layers like an onion.
Sheeting occurs when large igneous rock are exposed by erosion processes. As the overlying pressure is removed from the rock, it is allowed to expand and break off in layers like an onion.

Thermal expansion is another type of mechanical weathering that occurs when rocks exist in regions that have large daily temperature variations. Especially in deserts, heating during the day can cause rocks to expand. But at night, especially under clear skies, the temperature can drop significantly causing the rock to contract. The daily expansion and contraction can cause the rocks to weaken and break.
The final type of mechanical weathering is called biological activity. Plants and animals in their own way have the ability to break up rock. Plant roots searching for water and nutrients can grow into rock fractures, breaking down rock. Animals that can burrow can also move broken down rock toward the surface where more physical or even chemical weathering can initiate.
The final type of mechanical weathering is called biological activity. Plants and animals in their own way have the ability to break up rock. Plant roots searching for water and nutrients can grow into rock fractures, breaking down rock. Animals that can burrow can also move broken down rock toward the surface where more physical or even chemical weathering can initiate.
CHEMICAL WEATHERING
Chemical weathering is a more complex process than mechanical weathering. It's the chemical breakdown of the internal structure and mineral composition within rock. Water is by far the most important agent for chemical weathering. We will cover just a couple types of chemical weathering. Dissolution occurs when some types of minerals dissolve in water, much like sugar dissolves in liquid. One of the most water-soluble minerals is halite (also called salt). When halite dissolves within a rock, the rock structure can begin to break down. Water is also slightly acidic in nature, which has the ability to slowly corrose minerals. Carbonic acid and sulfuric acid can mix with precipitation creating acid precipitation that can dissolve rock material too.
Oxidation occurs when iron-rich minerals chemically interact with oxygen to create the red look iron oxide within some rocks. Because some electrons are lost in this weathering process, we say that that the rock has oxidized. Hydrolysis occurs when is a chemical reaction of any substance with water. The term hydro = water and lysis = a loosening. For example, when carbon dioxide dissolves in water, it forms carbonic acid, which can "eat away" and loosen the rock's mineral structure.
Chemical weathering is a more complex process than mechanical weathering. It's the chemical breakdown of the internal structure and mineral composition within rock. Water is by far the most important agent for chemical weathering. We will cover just a couple types of chemical weathering. Dissolution occurs when some types of minerals dissolve in water, much like sugar dissolves in liquid. One of the most water-soluble minerals is halite (also called salt). When halite dissolves within a rock, the rock structure can begin to break down. Water is also slightly acidic in nature, which has the ability to slowly corrose minerals. Carbonic acid and sulfuric acid can mix with precipitation creating acid precipitation that can dissolve rock material too.
Oxidation occurs when iron-rich minerals chemically interact with oxygen to create the red look iron oxide within some rocks. Because some electrons are lost in this weathering process, we say that that the rock has oxidized. Hydrolysis occurs when is a chemical reaction of any substance with water. The term hydro = water and lysis = a loosening. For example, when carbon dioxide dissolves in water, it forms carbonic acid, which can "eat away" and loosen the rock's mineral structure.
RATES OF WEATHERING
Several factors influence the rate at which rocks will weather down into sediment. The characteristics of the rock is an important factor because this takes into account factors like the chemical traits such as mineral composition and solubility of the minerals, and joints (cracks) within the rocks that can influence the ability of water to penetrate through it. Climate also plays a major role, particularly temperature and moisture. This can impact the frequency of some types of weathering such as ice wedging and growing seasons for biological activity in relation to weathering.
Climate can also influence chemical weathering. Where there is a lot of water, chemical weathering is likely to dominate, in arid regions, it will not. Human activity can also directly influence chemical weathering because humans can pollute the atmosphere and waterways, thus potentially creating acidic moisture.
Several factors influence the rate at which rocks will weather down into sediment. The characteristics of the rock is an important factor because this takes into account factors like the chemical traits such as mineral composition and solubility of the minerals, and joints (cracks) within the rocks that can influence the ability of water to penetrate through it. Climate also plays a major role, particularly temperature and moisture. This can impact the frequency of some types of weathering such as ice wedging and growing seasons for biological activity in relation to weathering.
Climate can also influence chemical weathering. Where there is a lot of water, chemical weathering is likely to dominate, in arid regions, it will not. Human activity can also directly influence chemical weathering because humans can pollute the atmosphere and waterways, thus potentially creating acidic moisture.
Mass Wasting
|
|
|
INFLUENCES ON LANDSLIDES
There are several factors that influence landslides, but ultimately it is a battle between friction and gravity. If friction is stronger than gravity for a particular slope, the soil will likely stay. But if gravity is stronger, the slope will fail.
The steeper the slope, the stronger the friction or rock strength must be to resist downslope motion. The steepest angle a slope can be before the ground will slide is about 30 degrees - called the angle of repose. Many times we will cut through a slope to make room for a road or other forms of development. So to help prevent the slope from sliding along these cut areas, retaining walls must be build. More on this later.
Another factor that determines landslides is the slope's material - what it is made of. Landslides are more prone on slopes that contain clay and shale. Without going into great detail here, the shape and composition of individual clay particles can absorb water and prevent water from peculating through the ground. A layer of clay on a slope can prevent water from filtering through the slope. Instead, the water stays near the surface and saturates the ground. This can cause the surface layers to lose friction and slide.
A third factor that influences whether a slope will fail is the load or weight of that slope. Adding weight to a weakened slope can obviously cause it to slide easier - especially on steep slopes. This added weight tends to occur by building on top of weak slopes, increasing the steepness of the slope, or over-saturating the slope.
Friction has been mentioned as a factor several times already, but there are a few more things must be said here. As already noted, as long as friction along the slope is stronger than gravity, the ground is unlikely to slide. But if that friction is weakened, slope fail becomes more likely. There are several other ways friction can be reduced along a slope: wildfires, removal of vegetation, or adding too much water.
Gravity is probably the ultimate driving force of landslides. The force of gravity pulls all things on the planet toward the center of the Earth. Without gravity, landslides would not occur. But unlike many of the other factors, humans have no influence or control on gravity.
WATER CONTENT WITHIN SLOPES
The amount of water in the soil is a major factor in the stability of a slope. When you build a sand castle, water is needed to build the walls and towers. That is because water has surface tension and is attracted to each other. This allows you to build towers greater than the angle of repose. So a little water can actually prevent slopes from sliding. But too much water lubricates the individual grains of sediment decreasing friction between each grain, so the possibility of landslides increases. The increase of water within the soils can come from over watering, pipe or swimming pool leaks, or prolonged stormy weather. In Utah and many mountainous regions, spring runoff of snow melt increases the water content within the soil. The following is a video from the USGS of the La Conchita, California landslide in 2005. Notice how well it flows down the mountainside. There are two reasons why this landslide occurred. First, this slide occurred on the same slope as a previous landslide in 1995. But the 2005 slide was also influenced by the fact that above is an orchard that was over-watering the vineyards and over-saturated the soil.
There are several factors that influence landslides, but ultimately it is a battle between friction and gravity. If friction is stronger than gravity for a particular slope, the soil will likely stay. But if gravity is stronger, the slope will fail.
The steeper the slope, the stronger the friction or rock strength must be to resist downslope motion. The steepest angle a slope can be before the ground will slide is about 30 degrees - called the angle of repose. Many times we will cut through a slope to make room for a road or other forms of development. So to help prevent the slope from sliding along these cut areas, retaining walls must be build. More on this later.
Another factor that determines landslides is the slope's material - what it is made of. Landslides are more prone on slopes that contain clay and shale. Without going into great detail here, the shape and composition of individual clay particles can absorb water and prevent water from peculating through the ground. A layer of clay on a slope can prevent water from filtering through the slope. Instead, the water stays near the surface and saturates the ground. This can cause the surface layers to lose friction and slide.
A third factor that influences whether a slope will fail is the load or weight of that slope. Adding weight to a weakened slope can obviously cause it to slide easier - especially on steep slopes. This added weight tends to occur by building on top of weak slopes, increasing the steepness of the slope, or over-saturating the slope.
Friction has been mentioned as a factor several times already, but there are a few more things must be said here. As already noted, as long as friction along the slope is stronger than gravity, the ground is unlikely to slide. But if that friction is weakened, slope fail becomes more likely. There are several other ways friction can be reduced along a slope: wildfires, removal of vegetation, or adding too much water.
Gravity is probably the ultimate driving force of landslides. The force of gravity pulls all things on the planet toward the center of the Earth. Without gravity, landslides would not occur. But unlike many of the other factors, humans have no influence or control on gravity.
WATER CONTENT WITHIN SLOPES
The amount of water in the soil is a major factor in the stability of a slope. When you build a sand castle, water is needed to build the walls and towers. That is because water has surface tension and is attracted to each other. This allows you to build towers greater than the angle of repose. So a little water can actually prevent slopes from sliding. But too much water lubricates the individual grains of sediment decreasing friction between each grain, so the possibility of landslides increases. The increase of water within the soils can come from over watering, pipe or swimming pool leaks, or prolonged stormy weather. In Utah and many mountainous regions, spring runoff of snow melt increases the water content within the soil. The following is a video from the USGS of the La Conchita, California landslide in 2005. Notice how well it flows down the mountainside. There are two reasons why this landslide occurred. First, this slide occurred on the same slope as a previous landslide in 1995. But the 2005 slide was also influenced by the fact that above is an orchard that was over-watering the vineyards and over-saturated the soil.
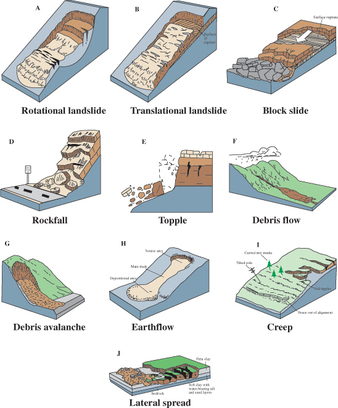
TYPES OF LANDSLIDES
A rock fall are the fastest of all landslide types and occurs when a rock falls through the air until it comes to rest on the ground - not too complicated. In Utah, they are common in the spring and fall because of what is called freeze-thaw weathering. In the daytime, temperatures in the spring and fall tend to be above freezing, which allows liquid water to enter cracks within rocks. At night, the temperatures cool below freezing and the water within the rocks freezes and expands which causes the rock to break more. The following morning, the ice will melt and go deeper within the crack to refreeze later that night. This freeze-thaw action over time can cause rocks to break off and fall to the ground. The debris the accumulates at the base of these steep slopes is called talus. But rock falls can also occur when heavy precipitation is falling on a steep slope, causing the rocks to lose friction and fall. The YouTube video on the right is a rock fall captured in Taiwan in late August 2013, following heavy precipitation in the region.
Rotational slides occur when the a landslide occurs in a curved manner concave to the sky. When this type of slide occurs, the upper surface of the slide tilts backwards toward the original slope and the lower surface moves away from the slope. They are common when the soil tends to be deep in clay or soft sediment deposits. The video on the right is a large landslide again in Taiwan in early September 2013 following every rainfall. Needless to say, they were having a bad few days in the region.
A rock fall are the fastest of all landslide types and occurs when a rock falls through the air until it comes to rest on the ground - not too complicated. In Utah, they are common in the spring and fall because of what is called freeze-thaw weathering. In the daytime, temperatures in the spring and fall tend to be above freezing, which allows liquid water to enter cracks within rocks. At night, the temperatures cool below freezing and the water within the rocks freezes and expands which causes the rock to break more. The following morning, the ice will melt and go deeper within the crack to refreeze later that night. This freeze-thaw action over time can cause rocks to break off and fall to the ground. The debris the accumulates at the base of these steep slopes is called talus. But rock falls can also occur when heavy precipitation is falling on a steep slope, causing the rocks to lose friction and fall. The YouTube video on the right is a rock fall captured in Taiwan in late August 2013, following heavy precipitation in the region.
Rotational slides occur when the a landslide occurs in a curved manner concave to the sky. When this type of slide occurs, the upper surface of the slide tilts backwards toward the original slope and the lower surface moves away from the slope. They are common when the soil tends to be deep in clay or soft sediment deposits. The video on the right is a large landslide again in Taiwan in early September 2013 following every rainfall. Needless to say, they were having a bad few days in the region.
|
|
|
Rather than rotating, a translational slide occurs when slope failure occurs parallel to the slope. Often times the slope failure occurs on soil composed of clay or shale, or along old fault lines, or previous slide areas. What makes translational slides dangerous is that they tend to flow faster and travel farther than rotational slides. The most expensive translational slide in U.S. history actually occurred in Thistle, Utah in 1983. The Utah Geologic Survey also provides a Google Earth file that looks at the Thistle landslide.
Debris flows are one of the most common, but most dangerous of the various types of landslides because of their speed and consistency. Debris flows tend to be a mixture of rock and water with two to three times the density of flooding streams. That density allows debris flows strip away the land and pick up objects as large as school buses. Debris flows are most common at the mouth of canyons along alluvial fans. Lets first explain an alluvial fan. When floods occur within the mouth of a canyon, either because of intense thunderstorms or snow melt, the erosive power of the water can pick up sediment and boulders - a debris flow. Now once the debris flow reaches the mouth of a canyon, the sediment gets deposited in a fan-shaped delta called an alluvial fan. The problem is that people like to live along alluvial fans because of their scenic view on the canyon. Another influence of debris flows are wildfires. When a wildfire strips an area of its vegetation, the bare soil is easily eroded away in either a thunderstorm or snow melt creating these debris flows. Because of Utah's topography and tendency to wildfires, debris flows are quite common.
Debris flows are one of the most common, but most dangerous of the various types of landslides because of their speed and consistency. Debris flows tend to be a mixture of rock and water with two to three times the density of flooding streams. That density allows debris flows strip away the land and pick up objects as large as school buses. Debris flows are most common at the mouth of canyons along alluvial fans. Lets first explain an alluvial fan. When floods occur within the mouth of a canyon, either because of intense thunderstorms or snow melt, the erosive power of the water can pick up sediment and boulders - a debris flow. Now once the debris flow reaches the mouth of a canyon, the sediment gets deposited in a fan-shaped delta called an alluvial fan. The problem is that people like to live along alluvial fans because of their scenic view on the canyon. Another influence of debris flows are wildfires. When a wildfire strips an area of its vegetation, the bare soil is easily eroded away in either a thunderstorm or snow melt creating these debris flows. Because of Utah's topography and tendency to wildfires, debris flows are quite common.

Lahars are essentially landslides caused by volcanic processes. Recall that volcanoes eject pyroclastic material ranging is size from ash to boulders. Now there tends to be two ways lahars occur. One is if a thunderstorm precipitates large amounts of moisture on the pyroclastic material and the pyroclastics flow downslope. The other option is if a volcano is snow-capped and the heat from the volcano causes some of the snow to melt and mix with the pyroclastic material. What makes lahars so dangerous is that they have the consistency of concrete and can travel hundreds of miles.
Summary
The earth's lithosphere may seem static and unchanging, but history has shown us otherwise. The planets crust is always in a state of creation and destruction. Those processes create slow erosional forces to create beautiful landscapes like Arches National Park and Zion National Park in southern Utah or the Grand Canyon in Arizona. But the earth can display destructive forces that are unimaginable to humans. The magnitude 7.0 earthquake that struck Haiti on January 12, 2010 was strong, but the catastrophic death toll of 100,000 to 300,000 (data varies) was because of the extremely poor economic situations and lack of building codes. Whereas the magnitude 9.1 earthquake in Japan on March 11, 2011 that generated the tsunami was 100 times more powerful in terms of ground shaking, but the death toll was much lower at around 16,000. Still an enormous catastrophe, but not to the extent of Haiti. Humans are constantly learning to live with and adapt to earth's tectonic forces as we expand into more ares of the planet.